A degree of preparation is needed for any of the photographic auto-digitizing techniques. For best results, use crisp images with well-defined subjects and strong contrasts.
1Scan or insert the photo you want to use. If you cannot see the image, turn on Show Bitmaps. See Loading bitmap artwork for details.

2Crop the image as necessary with the Crop Bitmap tools.
3Size the photo for its intended purpose. You may be prompted to resize when you run one of the PhotoStitch features.
4If your graphics application supports it, try re-sampling the image while resizing.
5Optionally, use Adjust Bitmap to adjust basic brightness and contrast.
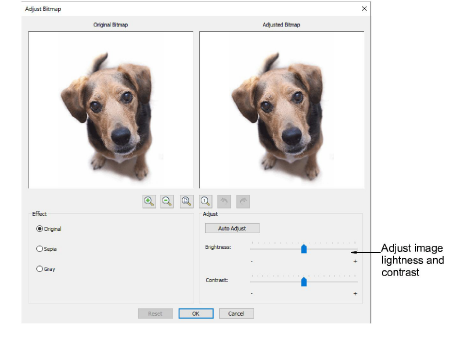
6First, try clicking Auto Adjust to allow the software to optimize image settings. Use Brightness and Contrast controls to sharpen the image further.
7Optionally, click Reset to return to default settings.
8Choose between image variations:
|
Option |
Function |
|
Sepia |
In photographic terms, ‘sepia’ refers to the dark-brown color of old-fashioned prints. Originally the process involved adding a pigment made from cuttlefish ink during development. |
|
Gray |
Grayscale images are ones composed exclusively of shades of gray, varying from black at the weakest intensity to white at the strongest. |
9Optionally, switch to Graphics Mode for alternative pre-processing.
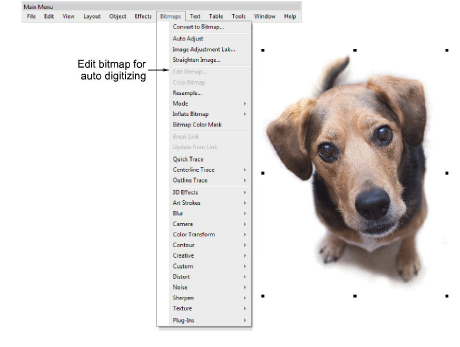
10For the full range of image adjustment techniques, use a dedicated graphics program like Corel PHOTO-PAINT®. If installed, the Edit Bitmap option is available.